One of the main issues that Google has tirelessly declared war on for years is duplicate content, for Google the term duplicate content refers to when there are pages that have different URLs that have the same content. There are also other cases in which search engines consider duplicate content such as:
- Different content but with urls identical to each other
- Session IDSs are often the creator of duplicate content. This occurs when each user visiting a website is assigned a different session ID that is stored in the url.
- Pages with HTTP, if our site uses the SSL encryption code, we can end up with an exact copy in our version that uses htpp.
- Pages followed by a pagination: this usually occurs on pages that share the same title and meta description.
- Identical Title and meta description in different pages of the same website.
- Your server is configured to display the same content for the subdomain with www or for the https protocol.
To avoid this serious problem, in February 2009 the major search engines such as Google and Yahoo found the holy grail, the well-known Rel=Canonical tags.
What is “Rel= Canonical” and what is it used for?
The “Rel= Canonical” tag is used to tell Google that one url is equivalent to another and that it should only index one of them.
For example, if we have url-page1 and url-page2, the latter being a copy of the former, using the rel=canonical tag we will tell the search engine that the url to be considered and indexed is url-page1.
Where is the “Rel=Canonical” placed?
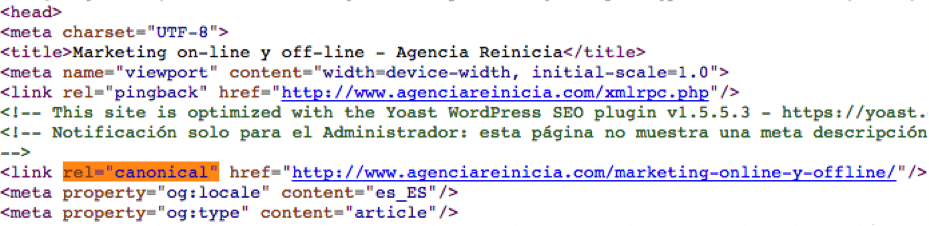
The tag “Rel=Canonical” should be placed between the start tags <head> and the closing </head> otherwise search engines would ignore the tag and we would be penalized for duplicate content. Following the previous example, it will have to be placed in both pages: url-page2 and url-page1. If there were 3 or more, it would have to be placed on ALL pages that could be considered duplicate content.
The link would be placed between the header tags as follows:
Canonicalization in case of different domains
When the same company has www.miempresa.com/es and www.miempresa.es both in Spanish but with different domains, we must choose the best domain for example www.miempresa.com/es and add the tag in www.miempresa.es in the following way:
<link rel=”canonical” href=”https://www.mipagina.com/es” />
With this we will tell Google that the domain page to be indexed is www.miempresa.com/es and not www.miempresa.es. Of course, this tag will have to be added in the pages that could be considered duplicates of both domains, NOT only in one of them.
Main errors in the use of the Rel=Canonical
Some of the most common errors when using the rel=canonical tag since its appearance are:
- Misusing relative url addresses instead of absolute url addresses:
- Incorrect: <link rel=”canonical” href=”/marketing-online-y-offline/”/>
- Correct: <link rel=”canonical” href=”https://new.agenciareinicia.com/marketing-online-y-offline/”/>
- Use the tag in the body of the page, i.e., in the <body>as mentioned above, the rel=canonical tag must be placed between the start tags. <head> and the closing</head>.
- Point to the first page of a paginated series. Suppose we have an article with several pages:
www.ejemplo.com/articulomanzana/pagina1,
www.ejemplo.com/articulomanzana/pagina2,
www.ejemplo.com/articulomanzana/pagina3
Placing the canonical url on page 2 or 3 to page 1 is not correct because they are not duplicate content, the use of rel=”canonical” in this case would make that pages 2 and 3 would not be indexed, for these cases it is advisable to use the markup pagination rel = “prev” and rel = “next”.
- Have several copies of the label.
- When we can access our website through different url’s such as: https://www.mipagina.com, https://mipagina.com, https://www.mipagina.com/index.php, although these url’s are considered different by Google, they show the same content and therefore we will be penalized for duplicate content. Therefore, if we find ourselves in a similar situation, it is convenient to choose the best version, which in this case is https://www.mipagina.com and redirect the other two versions, thus preventing Google from determining which is the best version. But in this case, the solution is NOT to indicate the canonical, but to make a complete 301 redirect from the “secondary” domain, for example, www.miempresa.com, to the preferred domain, for example, mycompany.com.
With this label the headache of duplicate content should no longer be a problem for a correct positioning of your website, and we can finally say that we have taken the lead to it, although we can never lose sight of it. We hope that with this article we have provided you with the necessary knowledge to make your website successful against malicious duplicate content.